The Effects of International Legislation on Global Trade: How Laws Shape Our Connected World
Have you ever wondered why your morning coffee costs what it does, or how that smartphone in your pocket made its way from a factory halfway around the world to your local store? The answer lies in a complex web of international legislation that governs global trade. These laws, agreements, and regulations don’t just exist in dusty legal textbooks – they actively shape the products we buy, the prices we pay, and the opportunities available to businesses worldwide.
International trade legislation serves as the invisible hand guiding trillions of dollars in commerce across borders every year. From the World Trade Organization’s multilateral agreements to bilateral trade deals between nations, these legal frameworks create the rules of engagement for our interconnected global economy. Understanding their impact isn’t just academic exercise – it’s essential for anyone who wants to grasp how our modern world truly works.

Understanding International Trade Legislation: The Foundation of Global Commerce
International trade legislation encompasses the vast array of laws, treaties, and agreements that govern how countries conduct business with one another. Think of it as the rulebook for the world’s largest game – one where the stakes involve jobs, economic growth, and national prosperity.
At its core, this legislation addresses fundamental questions: How much can countries tax imports? What safety standards must products meet? How should intellectual property be protected across borders? These aren’t abstract concerns – they directly influence whether a small business in Ohio can export to Europe, or whether consumers in Tokyo can access affordable goods from around the world.
The complexity of international trade law reflects the complexity of our global economy. A single product might contain components from dozens of countries, each governed by different regulations. A car manufactured in Mexico might use steel from South Korea, electronics from China, and leather from Brazil, all while being designed in Germany and sold in the United States. International legislation provides the framework that makes such intricate supply chains possible.
Key Players in International Trade Law: Who Makes the Rules?
The landscape of international trade legislation is populated by various organizations and agreements, each playing a crucial role in shaping global commerce. The World Trade Organization stands as perhaps the most influential player, serving as both a forum for trade negotiations and a dispute resolution mechanism when countries disagree.
Regional trade agreements have gained significant prominence in recent decades. The European Union represents one of the most integrated examples, where member countries have essentially created a single market with unified regulations. Similarly, agreements like the former NAFTA (now USMCA) have reshaped trade relationships between neighboring countries, demonstrating how regional legislation can have global implications.
Bilateral trade agreements between individual countries add another layer of complexity. When the United States negotiates a trade deal with Japan, or when the European Union strikes an agreement with Canada, these bilateral relationships can either complement or complicate the broader multilateral framework. It’s like having multiple sets of rules operating simultaneously, each with its own priorities and exceptions.
Positive Impacts of International Trade Legislation on Global Markets
When international trade legislation works effectively, the benefits ripple throughout the global economy in remarkable ways. Perhaps most significantly, these laws have facilitated an unprecedented expansion of global trade volumes. Since the establishment of the modern trade system after World War II, international commerce has grown exponentially, lifting millions out of poverty and creating opportunities that previous generations could never have imagined.
Standardization represents another crucial benefit. When countries agree on common technical standards, safety requirements, or quality measures, it becomes much easier for businesses to operate across borders. A pharmaceutical company that meets European safety standards can more easily enter other markets with similar requirements, reducing costs and accelerating the delivery of life-saving medications to patients worldwide.
The reduction of trade barriers has democratized global commerce in many ways. Small and medium-sized enterprises can now access international markets that were once the exclusive domain of large multinational corporations. A artisan jewelry maker in Thailand can sell directly to customers in Germany through e-commerce platforms, thanks partly to trade agreements that have simplified customs procedures and reduced tariffs.
Consumer benefits are equally impressive. International trade legislation has contributed to lower prices, greater product variety, and improved quality as companies compete on a global scale. The smartphone revolution, for instance, was only possible because international trade laws allowed for the complex global supply chains that make these devices both sophisticated and affordable.
Challenges and Negative Consequences of Trade Regulations
However, international trade legislation isn’t without its critics or negative consequences. One of the most contentious issues involves the impact on domestic industries and employment. When trade agreements make it easier to import goods from countries with lower labor costs, domestic manufacturers may struggle to compete, leading to factory closures and job losses in certain sectors.
The complexity of international trade law itself creates significant challenges, particularly for smaller businesses. Navigating the maze of regulations, compliance requirements, and documentation can be overwhelming and expensive. A small manufacturer might need to hire specialized legal counsel just to understand whether their products meet the requirements for export to a particular country.
Environmental concerns have become increasingly prominent in discussions about trade legislation. Critics argue that some trade agreements prioritize economic growth over environmental protection, potentially encouraging a “race to the bottom” where companies relocate to countries with weaker environmental standards. The challenge lies in balancing legitimate environmental concerns with the benefits of international commerce.
Cultural and social impacts also deserve consideration. As international trade expands, local industries and traditional ways of life can be disrupted. While this often leads to economic development, it can also result in the loss of cultural heritage and community identity, particularly in developing countries.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Legislative Impact
The North American Free Trade Agreement, and its successor the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement, provides a compelling case study in how trade legislation reshapes entire regions. Over nearly three decades, NAFTA fundamentally altered the economic relationship between the three North American countries, creating integrated supply chains and boosting overall trade volumes dramatically.
The automotive industry exemplifies this transformation. Today, a car assembled in the United States might cross the Mexican border multiple times during its production process, with different components being manufactured and assembled in the most cost-effective locations. This integration has made North American auto manufacturers more competitive globally, but it has also made the industry more vulnerable to disruptions in any one country.
Brexit offers another instructive example of how changes in trade legislation can create widespread uncertainty and economic disruption. The United Kingdom’s departure from the European Union forced businesses to navigate new customs procedures, regulatory requirements, and potential tariffs, demonstrating how deeply integrated modern economies have become and how disruptive changes to trade legislation can be.
The ongoing trade tensions between the United States and China illustrate how trade legislation can become a tool of broader geopolitical strategy. Tariffs, sanctions, and export controls have been used not just for economic purposes but also to address concerns about technology transfer, national security, and human rights. These cases show that international trade law operates within a broader context of international relations and domestic politics.
The Future of International Trade Legislation
Looking ahead, international trade legislation faces several emerging challenges that will likely reshape how global commerce operates. Digital trade represents perhaps the most significant frontier, as traditional trade laws struggle to address issues like data flows, digital services, and e-commerce platforms that operate across multiple jurisdictions simultaneously.
Climate change is driving new forms of trade legislation, including carbon border adjustments and sustainability requirements. The European Union’s proposed carbon border adjustment mechanism, for example, would impose charges on imports from countries with less stringent climate policies, potentially creating a new category of trade barrier based on environmental considerations.
Technological advancement continues to outpace legislative frameworks. Artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and automation are transforming how goods are produced, shipped, and tracked, but international trade laws often lag behind these innovations. Future legislation will need to address questions about algorithmic decision-making in trade, digital currencies, and the regulation of autonomous shipping and logistics systems.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also highlighted the vulnerability of global supply chains and raised questions about the balance between efficiency and resilience. Future trade legislation may place greater emphasis on supply chain security and the ability to maintain critical imports during global crises.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complex World of International Trade Law
International trade legislation represents one of the most powerful forces shaping our global economy, yet it often operates behind the scenes, invisible to the average consumer or business owner. These laws and agreements create the framework within which trillions of dollars in commerce flow across borders every year, affecting everything from the price of groceries to the availability of cutting-edge technology.
The effects of international trade legislation are neither uniformly positive nor negative – they represent trade-offs and choices about how to organize our global economy. While these laws have undoubtedly contributed to unprecedented economic growth and global integration, they have also created new challenges and inequalities that policymakers continue to grapple with.
As our world becomes increasingly interconnected, understanding the role of international trade legislation becomes ever more important. Whether you’re a business owner looking to expand internationally, a consumer curious about global supply chains, or simply someone trying to understand how our modern economy works, recognizing the profound impact of these legal frameworks is essential.
The future will likely bring new challenges and opportunities as technology, climate change, and shifting geopolitical relationships reshape the landscape of international trade. The legislation that emerges to address these challenges will continue to influence the prosperity of nations and the daily lives of billions of people around the world.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between bilateral and multilateral trade agreements?
Bilateral trade agreements involve two countries negotiating trade terms directly with each other, while multilateral agreements involve multiple countries. Bilateral agreements can be more tailored to specific relationships but may create complexity when countries have multiple overlapping agreements. Multilateral agreements, like those through the WTO, provide broader frameworks but may require more compromise among diverse interests.
How do international trade laws affect small businesses?
International trade laws can both help and challenge small businesses. On the positive side, they can reduce barriers to entry in foreign markets and provide standardized procedures. However, the complexity of compliance can be overwhelming for smaller companies that lack dedicated legal resources. Many trade agreements now include provisions specifically designed to help small and medium enterprises navigate international markets.
Can countries ignore international trade legislation?
While countries maintain sovereignty, ignoring international trade agreements typically comes with significant consequences. Other countries may impose retaliatory measures, access to certain markets may be restricted, and the offending country’s reputation in future negotiations may suffer. Most international trade disputes are resolved through established mechanisms rather than unilateral action.
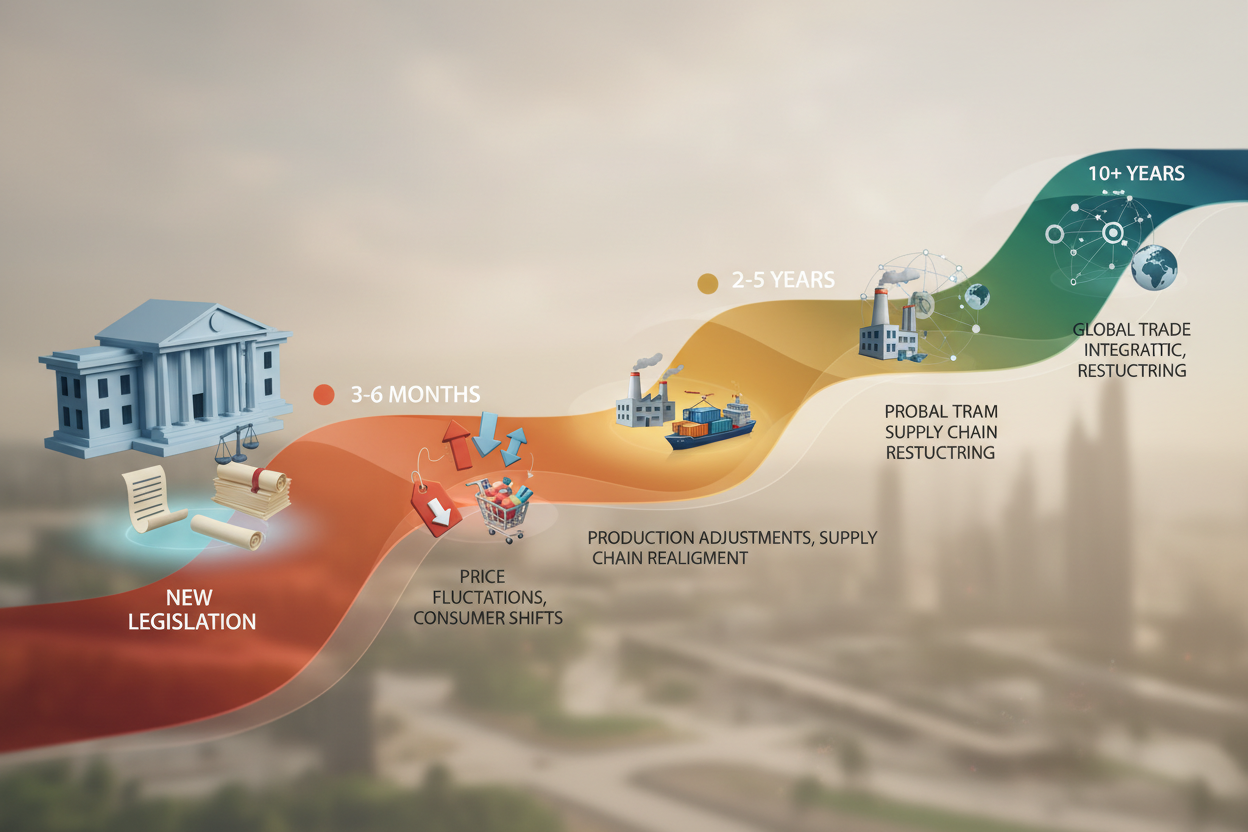
How long does it typically take for new trade legislation to show economic effects?
The timeline varies significantly depending on the type and scope of the legislation. Simple tariff changes might affect prices within months, while comprehensive trade agreements may take several years to show their full economic impact. Some effects, like changes in investment patterns or supply chain restructuring, may not become apparent for a decade or more.
What role do international trade laws play in addressing climate change?
International trade laws are increasingly incorporating environmental considerations. This includes provisions for environmental standards, restrictions on trade in certain environmentally harmful products, and mechanisms like carbon border adjustments. However, balancing trade liberalization with environmental protection remains an ongoing challenge in international negotiations.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.